The Science of Limestone Operations
From multiple levels of government ...
… to independent experts, geologists and seismologists.

Most blasting limits are based on a U.S. Bureau of Mines (USBM) report called RI 8507. The study established safe, science-based limits to prevent damage to even the most susceptible building materials.
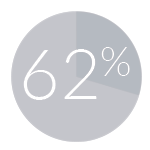
Florida’s ground vibration limits are 62% stricter than those set by USBM.

Mining operations in Florida are also regulated by the Florida State Fire Marshal’s Office.
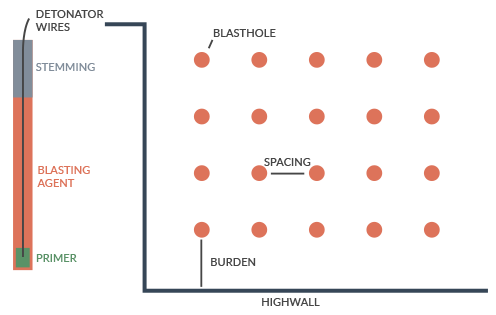
Step 1: Preparation
Document Review
Experts review everything from permit and project specifications to excavation plans and permitted blast times.

Site examination
Professionals must evaluate field conditions—from surface and groundwater to any geological irregularities.